Why Website Speed Matters in 2025? ✅ Full Optimization Checklist (2025 Ready) 1. Use Lightweight Theme Choose fast themes like: 2. Switch to Fast Hosting Use: 3. Enable Caching Install any of these: 4. Use CDN (Content Delivery Network) Recommended: 5. Minify HTML, CSS, JS WP Rocket, Autoptimize, or LiteSpeed Cache help with this. 6. Disable Unused Plugins Fewer plugins = better performance. Use “Query Monitor” plugin to find slow plugins. 7. Image Optimization Use: 8. Lazy Load Images & Iframes Built-in in WP 6.1+, or use caching plugin. 9. Remove Unused CSS/JS Use Flying Scripts or Perfmatters plugin. 10. Database Optimization 🛠 Pro Tips for Developers 📈 Real-World Speed Example Metric Before After Optimization Load Time 6.2s 1.8s Page Size 3.5 MB 0.9 MB Requests 120 43 Lighthouse Score 38 95 🔍 Tools You Should Bookmark 🔚 Final Words Website speed is no longer optional — it directly impacts SEO, user trust, and AdSense revenue. Agar aap WordPress developer hain ya blogger, toh abhi se hi apne site ko optimize kijiye.
Optimize and Manage Your WordPress Database Like a Pro
When it comes to WordPress performance, your database is the silent engine behind everything. From posts and pages to user accounts, settings, and plugin data — your WordPress site relies heavily on its MySQL database. Yet, it’s often the most overlooked aspect of performance and security. At wp-db.com, our mission is to help you unlock the full power of your WordPress database — efficiently, securely, and with confidence. Why Your WordPress Database Matters WordPress is built on a MySQL database structure that stores nearly all your content and settings. As your website grows, your database becomes bloated with: This excess data slows down query execution and increases server load, especially on high-traffic sites. Common WordPress Database Issues How to Optimize Your WordPress Database Here are some actionable tips to keep your database lean and healthy: 1. Regular Backups Before performing any optimization, back up your database using plugins like UpdraftPlus, WPVivid, or command-line tools like mysqldump. 2. Clean Up Post Revisions and Auto-Drafts Use tools like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner to safely delete post revisions, auto-drafts, and trashed items. sqlCopyEditDELETE FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type = ‘revision’; Always test queries on a staging environment before executing them live. 3. Optimize Tables MySQL’s OPTIMIZE TABLE command can reclaim unused space and defragment data: sqlCopyEditOPTIMIZE TABLE wp_posts, wp_comments, wp_options; Or use phpMyAdmin’s “Optimize Table” feature for a visual interface. 4. Control Autoloaded Data Check which options are autoloaded by default and remove any that aren’t needed. Autoload bloat is a common culprit behind slow dashboards. 5. Schedule Automated Cleanups Don’t wait for things to slow down — schedule weekly or monthly cleanups using plugins or custom cron jobs. Tools We Recommend At wp-db.com, we test and review plugins, scripts, and methods for optimizing your database. Some of our favorites:
Struggling with a Slow WordPress Website? Here’s How to Fix It
WordPress is a fantastic platform for building websites, but one common issue many users face is slow performance. A sluggish website can drive visitors away, hurt your SEO rankings, and ultimately affect your business. If you’re struggling with a slow WordPress site, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Let’s break down the reasons behind the slowdown and how to fix them. 1. Choose a Reliable Hosting Provider Your hosting plays a crucial role in website speed. Cheap shared hosting might save you money initially, but it can slow your site significantly. Consider upgrading to: 2. Use a Lightweight Theme Many WordPress themes come with unnecessary features that bloat your site. Choose a well-coded, lightweight theme like GeneratePress, Astra, or Hello Elementor. 3. Optimize Images Large images can drastically slow down your site. Use plugins like: Compress images before uploading and use modern formats like WebP for better performance. 4. Install a Caching Plugin Caching significantly improves loading speed by storing a static version of your site. Popular caching plugins include: 5. Minimize Plugins Too many plugins can slow your site down. Audit your installed plugins and remove any that are unnecessary. Stick to well-coded and lightweight plugins. 6. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) A CDN helps distribute your website’s content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing load times. Some popular options are: 7. Optimize Your Database Over time, your WordPress database accumulates unnecessary data like post revisions, spam comments, and transients. Use plugins like WP-Optimize to clean it up and improve performance. 8. Disable Unused Scripts and Styles Many plugins and themes load unnecessary CSS and JavaScript files. Use plugins like Asset CleanUp or Perfmatters to disable unwanted scripts on specific pages. 9. Enable Lazy Loading Lazy loading ensures images and videos are only loaded when they appear in the user’s viewport. WordPress has a built-in lazy loading feature, but plugins like a3 Lazy Load can further enhance it. 10. Keep Everything Updated Outdated themes, plugins, and WordPress versions can slow down your site and create security vulnerabilities. Regularly update everything to ensure optimal performance.
How to Delete All WordPress Posts Except Specific Ones (Code-Based Approach)
Managing a WordPress site sometimes requires bulk deletion of posts, while keeping a few important ones. Instead of manually deleting posts one by one, you can automate the process using code. In this guide, we’ll explore how to delete all WordPress posts except specific ones using PHP and WP CLI. Why Bulk Deleting Posts Might Be Necessary? Instead of using plugins, a custom script or WP CLI command provides more control and efficiency. Method 1: Using PHP (WP_Query & wp_delete_post) You can add the following function to your functions.php file or execute it through a custom plugin or a code snippet plugin. function delete_all_posts_except($exclude_ids = array()) { if (empty($exclude_ids)) { $exclude_ids = array(); // Ensure it’s an array } $args = array( ‘post_type’ => ‘post’, // Change to ‘any’ to delete all post types ‘post_status’ => ‘any’, ‘posts_per_page’ => -1, ‘post__not_in’ => $exclude_ids, ); $query = new WP_Query($args); if ($query->have_posts()) { while ($query->have_posts()) { $query->the_post(); wp_delete_post(get_the_ID(), true); // True for force delete } } wp_reset_postdata();}// Call function with post IDs you want to excludedelete_all_posts_except(array(10, 20, 30)); // Replace with your actual post IDs Method 2: Using WP CLI (Faster & More Efficient) wp post delete $(wp post list –post_type=post –format=ids | grep -v -E ’10|20|30′) wp post list –post_type=post –format=ids lists all post IDs. grep -v -E ’10|20|30′ excludes the specified post IDs. wp post delete removes all other posts permanently.
How to Optimize Your WordPress Database Without Losing Useful Data
A well-optimized database is crucial for maintaining the performance of your WordPress website. Over time, unnecessary data accumulates in the database, making it bloated and slowing down your site. However, optimizing the database without losing essential data requires a careful and strategic approach. This guide will help you understand the best practices to optimize your WordPress database safely. Why Optimize Your Database? Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Your WordPress Database 1. Backup Your Database Before making any changes, ensure you have a complete backup of your WordPress database. Use tools like: This step is non-negotiable as it ensures you can restore your site in case something goes wrong 2. Remove Unused Data Certain types of data can accumulate in your database without being actively used. Removing them can reduce database size significantly. 3. Optimize Database Tables Over time, database tables can become fragmented. Optimizing these tables reorganizes the data and improves query performance. 5. Use Database Cleanup Plugins Several plugins are designed to clean and optimize WordPress databases. Popular options include: These plugins often provide options to review the data before deletion, ensuring that you retain useful information. 6. Remove Orphaned Metadata Orphaned metadata includes leftover data related to deleted posts, users, or comments. Tools like WP-Optimize and Advanced Database Cleaner can identify and remove such metadata without affecting active data. 7. Optimize Database Queries Poorly written database queries can slow down your site. Use a query monitoring tool like Query Monitor to: 8. Consider Database Indexing Adding indexes to frequently queried database columns can improve performance. However, this requires technical knowledge. Consult with a developer or database expert to implement indexing safely. 9. Use a Dedicated Database Hosting Solution If your website handles large amounts of data or high traffic, consider: 10. Regular Maintenance Database optimization is not a one-time task. Schedule regular maintenance to keep your database lean and efficient. Many plugins offer scheduling features for automated optimization. Additional Tips for Safe Database Optimization How to Optimize Your WordPress Database Without Losing Useful Data.
10 Steps to Secure Your WordPress Website from Hackers
1. Keep WordPress Core, Plugins, and Themes Updated Outdated software is one of the most common vulnerabilities hackers exploit. Regular updates not only bring new features but also patch security loopholes. 2. Use Strong Passwords and Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Weak passwords are a common entry point for hackers. Strengthen access controls to protect your admin area. 3. Limit Login AttemptsPrevent brute-force attacks by limiting the number of login attempts a user can make. 4. Secure the Login Page The WordPress login page is a common target for attackers. Securing it can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. 5. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF) A firewall acts as the first line of defense, blocking malicious traffic before it reaches your website. 6. Implement Secure Hosting Practices Choosing the right hosting provider can make or break your website’s security. 7. Regularly Back Up Your Website Backups are essential for disaster recovery. They ensure you can quickly restore your site in case of a breach. 8. Monitor and Audit User Activity Track changes made by users on your site to detect suspicious activities. 9. Harden WordPress Security Settings Fine-tuning your WordPress configuration can block common attack vectors. 10. Conduct Regular Security Audits Routine security audits help identify and address vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. Bonus Tips
How to Debug WordPress Like a Pro: Tools and Techniques
Foundational Debugging Principles Reproducibility is Key Before embarking on any debugging journey, ensure you can consistently reproduce the issue. This eliminates inconsistencies and narrows down potential causes. Isolate the Problem Leverage the Power of Logs Debugging Tools for WordPress 1. WP_DEBUG The WP_DEBUG constant is a built-in debugging tool in WordPress. By enabling it, you can log and display PHP errors, notices, and warnings. 2. Query Monitor Query Monitor is a powerful plugin for debugging database queries, PHP errors, hooks, and more. It provides detailed insights into what’s happening on your WordPress site. 3. Log Files Server logs (such as Apache or Nginx logs) and PHP error logs are essential for diagnosing issues that don’t appear in the WordPress interface. 4. Browser Developer Tools Built into modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge, these tools help debug frontend issues such as CSS conflicts, JavaScript errors, and performance bottlenecks. 5. PHPStorm or VS Code with Xdebug For in-depth debugging, integrating an IDE like PHPStorm or Visual Studio Code with Xdebug is a game-changer. Xdebug allows you to step through your code, set breakpoints, and inspect variables in real time. 6. Error Monitoring Services Tools like Sentry or New Relic provide real-time error monitoring and reporting, making them ideal for production environments. 7. Debug Bar and Related Plugins The Debug Bar plugin adds a debugging menu to the admin bar, displaying useful information such as query performance, memory usage, and error messages. Advanced Debugging Techniques 1. Step Debugging with Xdebug 2. Analyze Hooks and Filters WordPress’s hook system is powerful but can sometimes lead to conflicts. Use tools like Query Monitor or Debug Bar to trace which hooks are being executed. 3. Profile Performance Debugging Specific Issues 1. White Screen of Death (WSOD) 2. 500 Internal Server Error 3. Database Issues Best Practices for Proactive Debugging
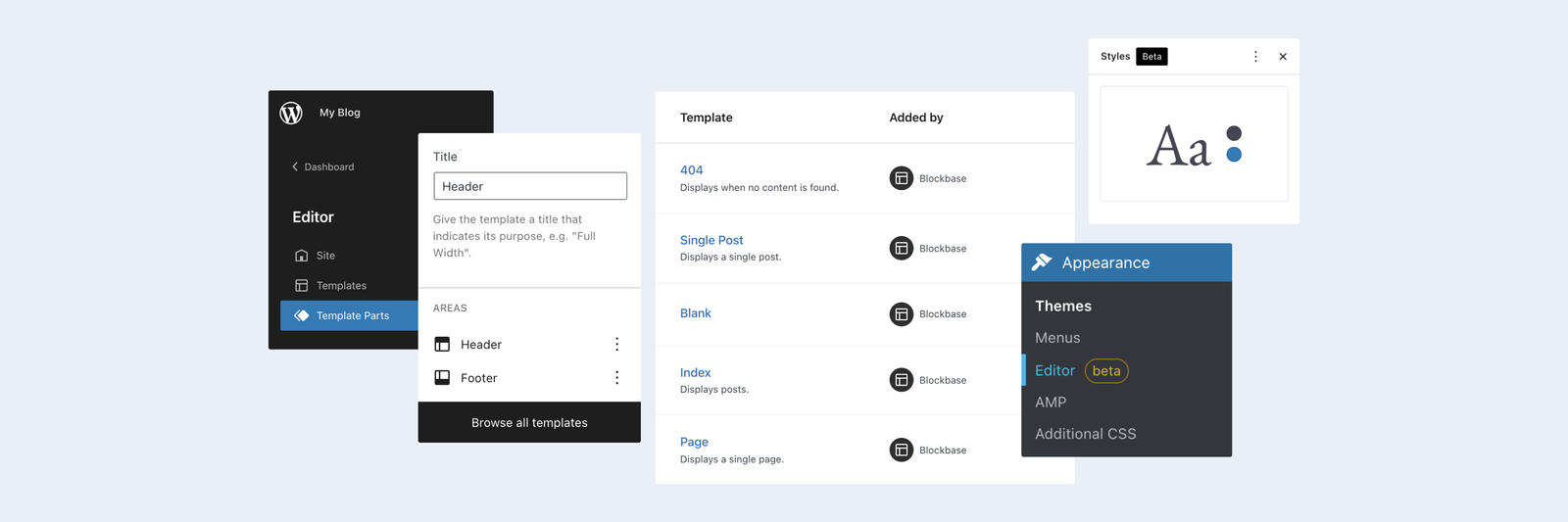
Exploring the Future of WordPress with Full Site Editing (FSE)
WordPress, the world’s most popular content management system (CMS), continues to evolve, and one of its most transformative advancements is Full Site Editing (FSE). Built upon the Gutenberg block editor, FSE empowers users with unprecedented control over the design and functionality of their websites. This revolutionary feature set marks a paradigm shift, moving beyond traditional theme constraints and enabling a more fluid and intuitive website-building experience. What is Full Site Editing? Full Site Editing (FSE) is a suite of features that allows users to design and customize their entire website using blocks—the foundational elements of the Gutenberg editor. Unlike the traditional WordPress experience, where themes and PHP templates dictated much of the site’s design, FSE puts the power back into the hands of users. With FSE, every part of a site—headers, footers, sidebars, and even archives—can be edited visually, in real-time, without needing to touch code. By leveraging reusable blocks and block-based themes, FSE offers a flexible, user-friendly way to build unique and customized layouts. This evolution opens doors for both developers and non-technical users to create professional-grade websites more efficiently. Key Features of Full Site Editing The Benefits of Full Site Editing The Future of WordPress with FSE Full Site Editing is an ongoing development, with new features and enhancements continually being introduced. As the WordPress ecosystem evolves around FSE, we can anticipate exciting innovations in website design and functionality: Challenges and Limitations